Several months ago, I put together this syllabus for use in a future seminar course Law as a Complex System. This contains far more content than would be practical for the typical 2 credit seminar. However, I have decided to repost this because it could also serve as a reading list for anyone who is interested in learning more about the methodological tradition from which must of our scholarship is drawn. If you see any law related scholarship you believe should be included please feel free to email me.
Author: clsadmin
Law as a Seamless Web?
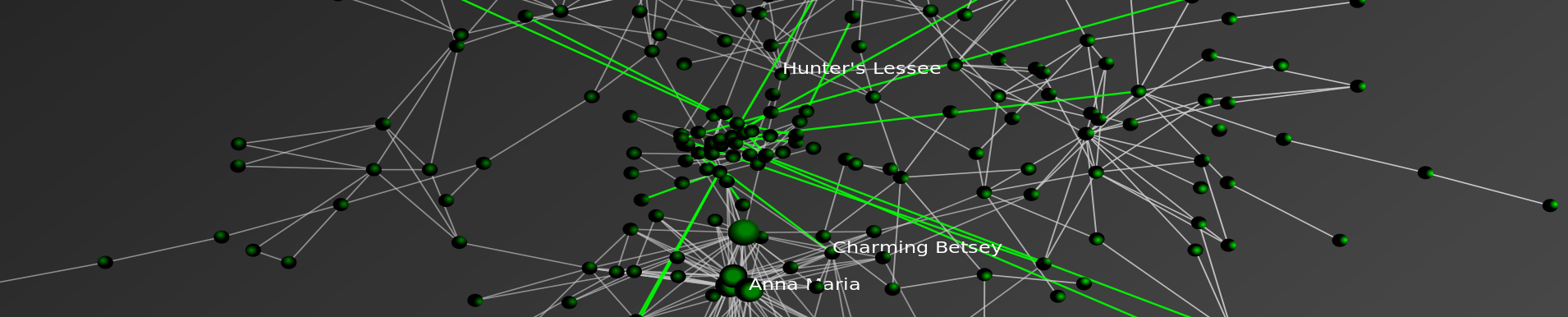
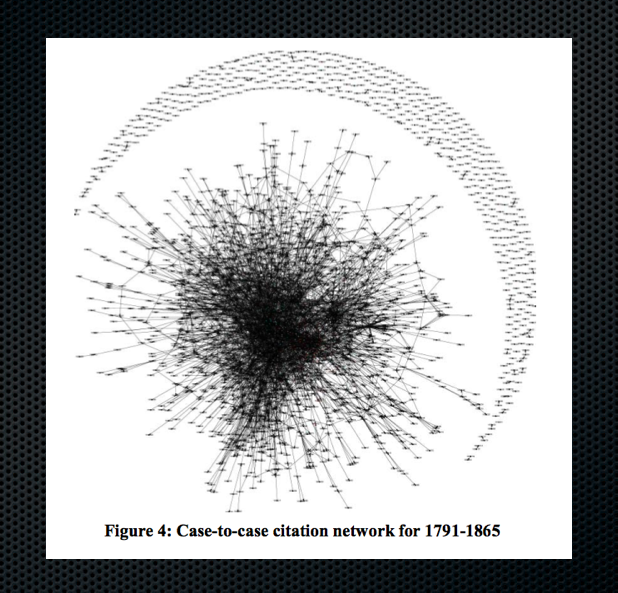
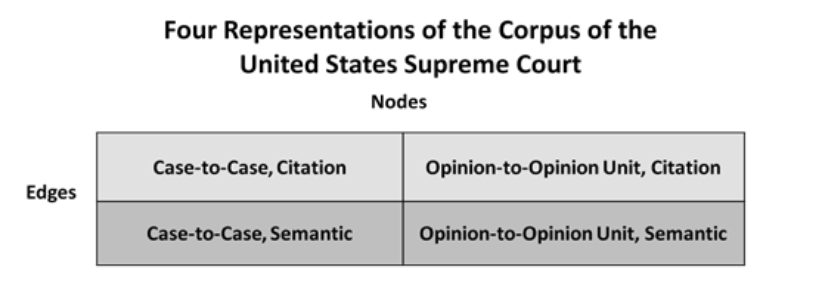
We have recently posted Law as a Seamless Web? Comparison of Various Network Representations of the United States Supreme Court Corpus (1791-2005) to the SSRN. Given this is the first of several posts about the paper, I will speak broadly and leave details for a subsequent post. From the abstract “As research of judicial citation and semantic networks transitions from a strict focus on the structural characteristics of these networks to the evolutionary dynamics behind their growth, it becomes even more important to develop theoretically coherent and empirically grounded ideas about the nature of edges and nodes. In this paper, we move in this direction on several fronts …. Specifically, nodes represent whole cases or individual ‘opinion units’ within cases. Edges represent either citations or semantic connections.” The table below outlines several possible network representations for the USSC corpus.
The goal of the paper is to do some technical and conceptual work. It is a small slice of broader project with James Fowler (UCSD) and James Spriggs (WashU). We recently presented findings from the primary project at the Networks in Political Science Conference. The main project is entitled The Development of Community Structure in the Supreme Court’s Network of Citations and we hope to have a version of this paper on the SSRN soon. In the meantime, we plan additional discussion of Law as a Seamless Web in the days to come.
Iranian Blogosphere: Followup from Harvard NIPS 2009
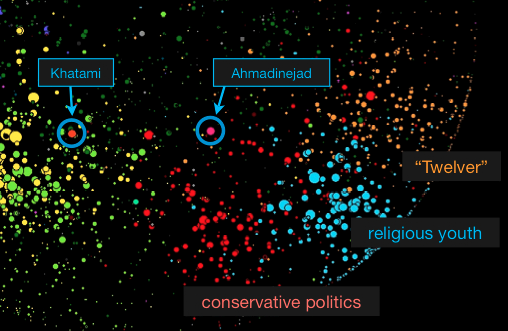
We genuinely enjoyed our trip to Boston for the Networks in Political Science 2009 Conference at Harvard. There were many highlights but given the timely nature of their work we wanted to highlight the presentation by John Kelly & Bruce Etling entitled Mapping Culture, Politics, and Religion in the Arabic Blogosphere. This is a followup to last year’s presentation, Mapping Iran’s Online Public: Politics and Culture in the Persian Blogosphere. As usual, the folks at the Berkman Center are doing great work. Check out today’s New York Times featuring an article entitled Iranian Blogosphere Tests Government’s Limits.
Harvard Political Networks Conference
It was a long trip but we are looking forward to an exciting day of presentations at tomorrow’s Harvard Political Networks Conference. Check out the program! We hope to see you there.
Artificial Intelligence and Law — Barcelona 2009
Live from Barcelona, we are on the road at the International Association for Artificial Intelligence and Law. Henry Prakken has just delivered the keynote address and we will soon be giving our presentation. The conference is interesting as it embraces a wide range of topics and intellectual traditions. For example, there is a significant emphasis on ontological reasoning, computational models of argumentation and the use of XML schemas. In addition, there are a number of folks using graph theoretic techniques and applying them to the development of the law. It has been a nice few days and we have enjoyed our time here. Tomorrow, the trip continues….
On the Road Again… Trip to Colorado Law School
We just finished a few very interesting days at Colorado Law School. Given the intersect of Computer Program and Law is a fairly narrow set, it was great to spend sometime time at CU Law School because its faculty features two scholars with a significant programming background — Paul Ohm and Harry Surden.
In addition to discussing CLS, we participated in a workshop on New Institutional Economics (NIE) and Law. I found this workshop very interesting as outside of my work in Computational Legal Studies, I have authored scholarship at the crossroads of New Institutionalism and Constitutional Political Economy. For example, I have this article and this work in progress. My work follows the tradition of the Bloomington School of NIE. In two weeks, I will be presenting work in progress at ISNIE in Berkeley.
Following the Colorado NIE Workship, we participated in the Silicon Flatirons Government 3.0 roundtable. I do not want to preempt the forthcoming white paper but I will say that it was a very worthwhile discussion. It solidified my views on some topics and changed my mind on some others. So, the road show continues… AI & Law in Barcelona starts tomorrow… so light blogging for the next week. But as I like to say… more to come…
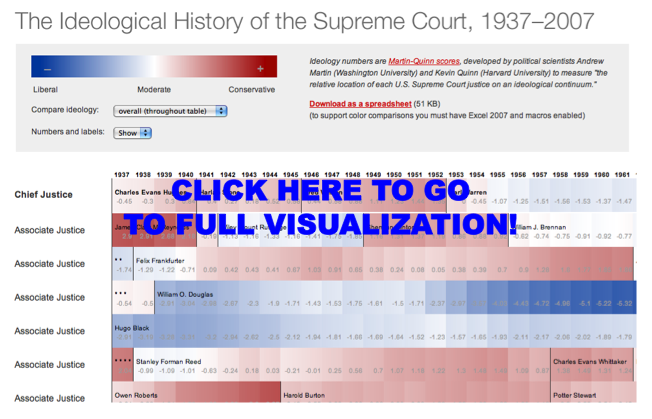
Visualization of the Ideological History of the Supreme Court
Here is a cool visual for the Martin-Quinn Scores. For those of you not familiar, the Martin-Quinn paper and “MQ Scores” represented a significant breakthrough in the field of judicial politics. On that note, Stephen Jessee & Alexander Tahk have done a nice job both bringing their data up to date and extending their work. For those interested, click on the visual above and check out all of the relevant links contained within this post.
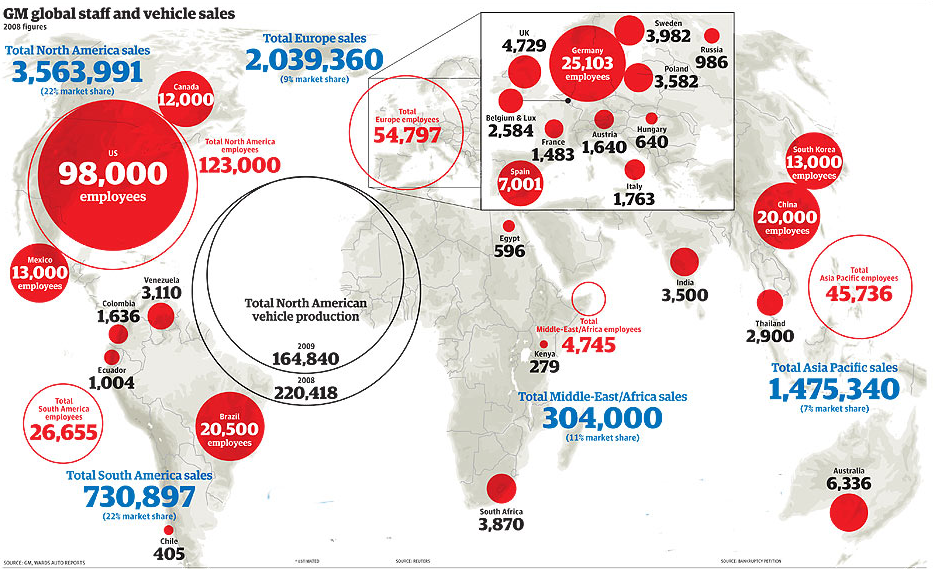
The General Motors Corp. [From the Guardian]
On this tough day here in Michigan … here is the visualization from the Guardian. Bracketing poor performance in the domestic market, there are some bright spots here in the company’s worldwide sales.
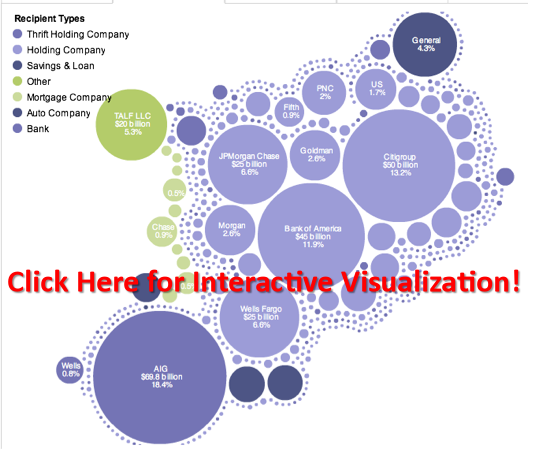
Tracking the TARP [From Information Aesthetics]
Information Aesthetics is now highlighting Subsidyscope — a project designed to track how various institutions receive federal monies. Of particular interest is their visualization of disbursements under the Troubled Asset Relief Program (TARP). Sponsored by the PEW Charitable Trust, the site also contains .csv files for most of the underlying data.
An Exchange in Need of Empirics and an Analytical or Computational Model
On a recent flight, I read Jeffrey Toobin’s New Yorker Article on Chief Justice Roberts entitled “No More Mr. Nice Guy”. The exchange quoted above is drawn from this article. While I believe it is appropriate to engage empirical data where available, the underlying discussion is not one exclusively subjectable to empirical inquiry. Rather, it is, at least in part, a question in need of a formal theoretic model. Justice Roberts and Mr. Katyal are implicitly discussing a “state of the world” not yet realized but which would be realized if the statute were not to exist. What would benefit the discussion is principled manner to adjudicate between these two inferences drawn above. Namely, it would be useful to fully evaluate what behavior would likely follow if the statute were not to exist.
There exist a variety of mathematical modeling techniques which could inject some much needed rigor into the above discussion. To my knowledge, such an applied model has yet to be offered. The Supreme Court’s decision in the matter is soon forthcoming. Given the nature of the exchange above, there is reason to believe that if Chief Justice Roberts prevails ….we will get our model as the “state of the world” discussed above will no longer be hypothetical….
Data.gov is Now Online
Important thing worth noting … data.gov went online during our break …. From the front page “The purpose of Data.gov is to increase public access to high value, machine readable datasets generated by the Executive Branch of the Federal Government. Although the initial launch of Data.gov provides a limited portion of the rich variety of Federal datasets presently available, we invite you to actively participate in shaping the future of Data.gov by suggesting additional datasets and site enhancements to provide seamless access and use of your Federal data. Visit today with us, but come back often. With your help, Data.gov will continue to grow and change in the weeks, months, and years ahead.”
Marginal Returns and the Mechanics of a Computational Legal Study
As noted earlier, we imposed a break over the Memorial Day Weekend and hope to return to a regular posting schedule this week. For the first post of the week, we want to reach out to readers exclusively socialized in legal or traditional social scientific circles. Namely, we recognize that a number of the approaches highlighted herein are not currently within the mainstream. Thus, many may not be familiar with the methods presented on this blog. So, just to reset ….
On this blog, we discuss scholarship or projects applying a computational, complex systems or informatics approach to questions of potential interest to legal and/or social science scholars. Our approach is unappolgetically interdisciplinary as we attempt to weave together a wide range of scientific methods and intellectual traditions. We have or will feature relevant scholarship from computer science, physics, network science, empirical legal studies, information visualization, new social history, computational politics and economics, mathematical sociology, behavioral biology, neuroscience, anthropology, linguistics ….
We have deeper motivations — but at a minimum — we believe the embrace of the techniques presented herein is justified as a search for intellectual returns on investment. While not applicable to all substantive questions, where appropriate we believe our approach to scholarship can convert higher-hanging fruit into low-hanging fruit.
It is hardly a revelation to note that disciplines tend to be insular. They develop cultures of intellectual reenforcement that can operate to stymie innovation by punishing deviations from status quo practices. Recognizing that switching costs are non-trivial, we want to once again highlight two articles previously discussed on this blog. For those interested in exploring a different terrain, we believe these articles offer both the rationale for and some of the mechanics of a computational approach to legal studies.
The first article, drawn from a recent issue of Science Magazine and authored by some of the leaders in field, highlights some of the possibilities of and potential perils associated with a computational revolution in the social sciences. It is a call to arms to many in social science circles. In a similar vein, Paul Ohm’s forthcoming article represents the law review analog. Among other things, Professsor Ohm offers a concrete playbook for those interested in applying the relevant mechanics to some discrete question of interest. The code displayed above is drawn from his article.
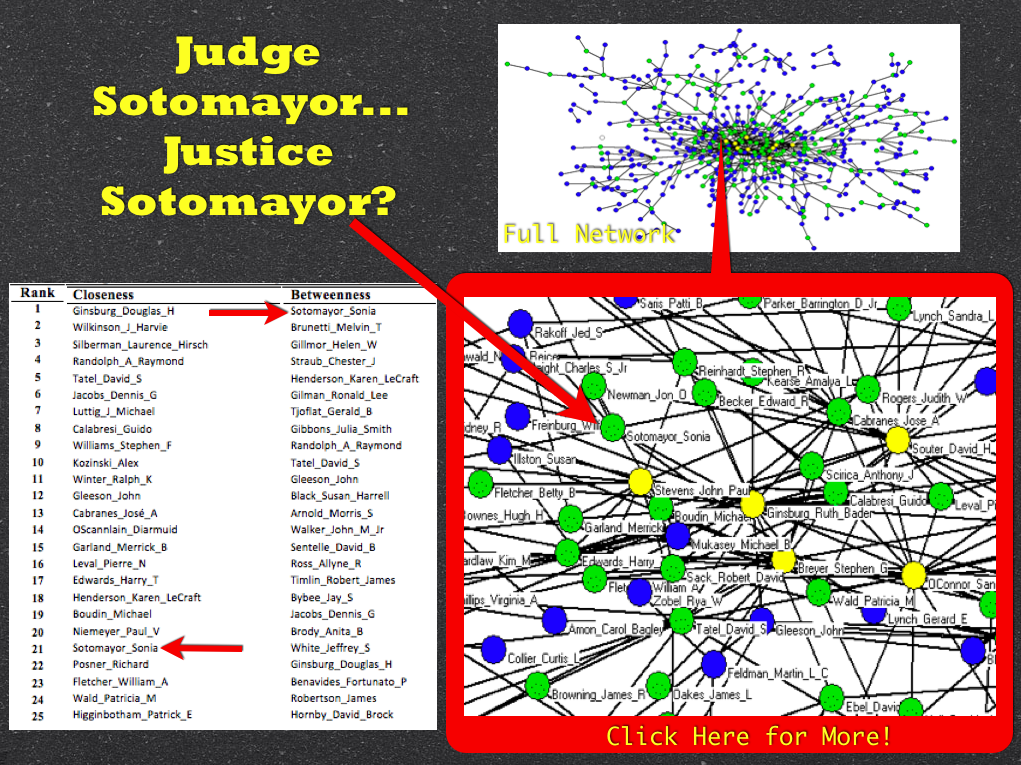
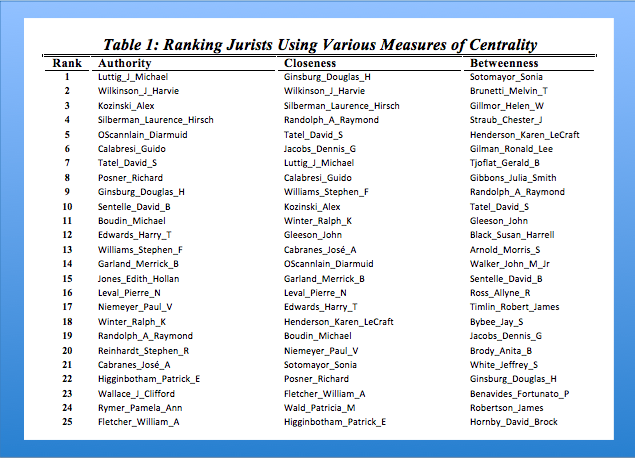
Measuring the Centrality of Federal Judges
Above are some graph statistics from our paper Hustle and Flow: A Social Network Analysis of the American Federal Judiciary. The paper measures the aggregated window of 1995-2005. These, of course, are not the only measures of centrality but they are commonly used in the network science literature. If you are interested — click through to the paper for a description of how these measures are calculated.
We believe these and other elements of the paper offer a good cut on the question of social prestige within the American Federal Judiciary. For example, in the paper we offer a graph visualization where Judge now Justice Alito as well as Judge turned Attorney General Michael Mukasey occupy an extremely central social position (just outside of the Top 25). We think this is useful because their social prestige is measured at a time period prior to their respective nominations. With appropriate control variables for the respective office in question … perhaps we might have been able to predict their nomination?
For purposes of the current Supreme Court opening and conditioned on the selection of a lower court justice with “blue team” credentials, we believe these graph statistics indicate Judge Sonia Sotomayor, Judge Merrick Garland , Judge William Fletcher & Judge David Tatel all occupy high levels of social prestige among their fellow judges and justices. Debate regarding qualifications of various individuals is likely to continue. While certainly not dispositive, we thought it appropriate to offer some social scientific evidence on the question.
President Obama might go outside the tradtional Federal Court of Appeals judge on this round. For example, Governor Jennifer Granholm, Solicitor General Elena Kagan and Homeland Security Secretary Janet Napolitano appear to be on the short list. However, keep these names in mind as this is probably not President Obama’s last nomination to the high court.