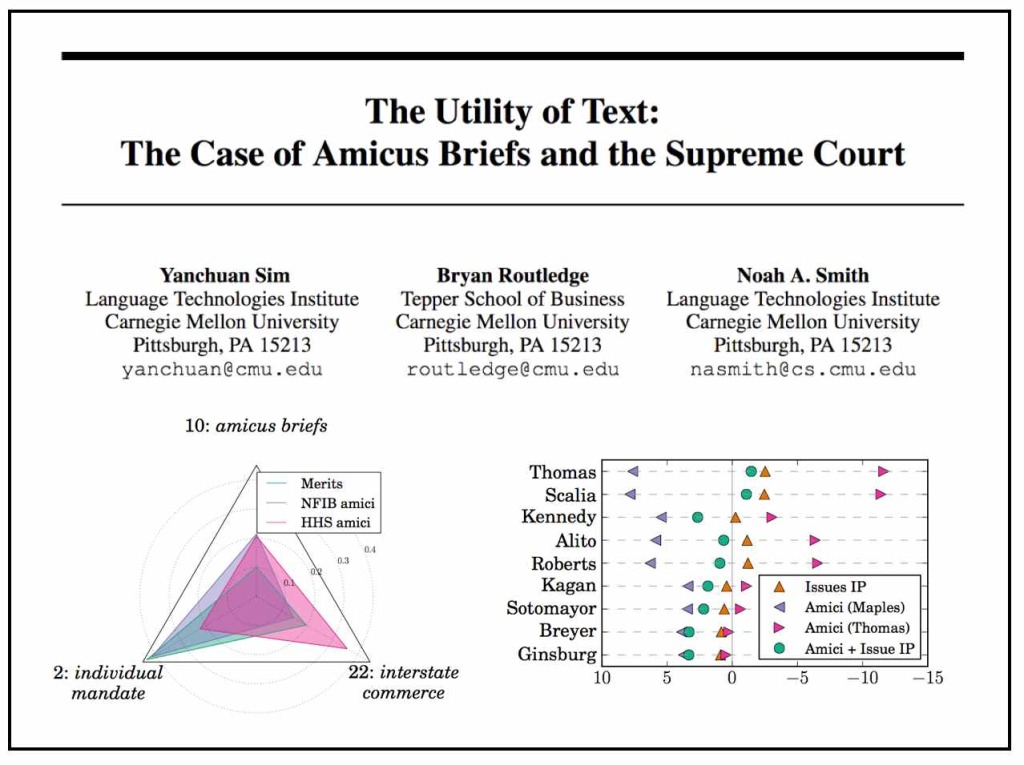
 From the Abstract: “We explore the idea that authoring a piece of text is an act of maximizing one’s expected utility. To make this idea concrete, we consider the societally important decisions of the Supreme Court of the United States. Extensive past work in quantitative political science provides a framework for empirically modeling the decisions of justices and how they relate to text. We incorporate into such a model texts authored by amici curiae (“friends of the court” separate from the litigants) who seek to weigh in on the decision, then explicitly model their goals in a random utility model. We demonstrate the benefits of this approach in improved vote prediction and the ability to perform counterfactual analysis. (HT: R.C. Richards from Legal Informatics Blog)
From the Abstract: “We explore the idea that authoring a piece of text is an act of maximizing one’s expected utility. To make this idea concrete, we consider the societally important decisions of the Supreme Court of the United States. Extensive past work in quantitative political science provides a framework for empirically modeling the decisions of justices and how they relate to text. We incorporate into such a model texts authored by amici curiae (“friends of the court” separate from the litigants) who seek to weigh in on the decision, then explicitly model their goals in a random utility model. We demonstrate the benefits of this approach in improved vote prediction and the ability to perform counterfactual analysis. (HT: R.C. Richards from Legal Informatics Blog)