Year: 2011
My Slides from New and Emerging Legal Infrastructures Conference (NELIC) [ @ Berkeley Law ]
UPDATED SLIDES – Midwest Law & Econ Association – Indiana Law – Sept 2011
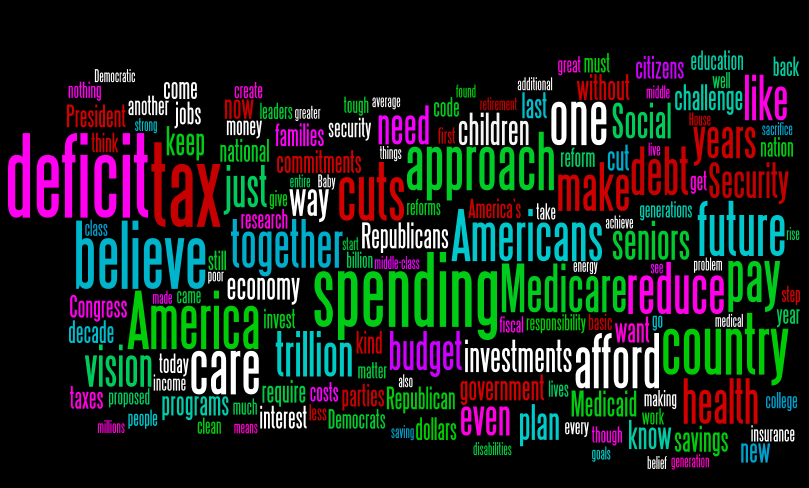
Wordle of President Obama’s Budget Speech at George Washington University
I realize that Wordles are not among the most scientific things on the planet (see Drew Conway’s post on this point over at ZIA). However, I just thought I would play around with President Obama’s speech on the budget delivered today at George Washington University. See above …
Building a Better Legal Search Engine, Part 1: Searching the U.S. Code
Cross Post from Michael Bommarito’s Blog – “ Last week, I mentioned that I am excited to give a keynote in two weeks on Law and Computation at the University of Houston Law Center alongside Stephen Wolfram, Carl Malamud, Seth Chandler, and my buddy Dan Katz from here at the CLS Blog. The first part in my blog series leading up to this talk will focus on indexing and searching the U.S. Code with structured, public domain data and open source software.
Last week, I mentioned that I am excited to give a keynote in two weeks on Law and Computation at the University of Houston Law Center alongside Stephen Wolfram, Carl Malamud, Seth Chandler, and my buddy Dan Katz from here at the CLS Blog. The first part in my blog series leading up to this talk will focus on indexing and searching the U.S. Code with structured, public domain data and open source software.
Before diving into the technical aspects, I thought it would be useful to provide some background on what the U.S. Code is and why it exists. Let’s start with an example – the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act. After the final version of HR 4173 was passed by both houses and enrolled in July of 2010, it received a new identifier, Public Law 111-230. This public law, along with private laws, resolutions, amendments, and proclamations, is published in order of enactment in the Statutes at Large. The Statutes at Large is therefore a compilation of all these sources of law dating back to the Declaration of Independence itself, and as such, is the authoritative source of statutory law.
If we think about the organization and contents of the Statutes at Large, it quickly becomes clear why the Code exists. The basic task of a legal practitioner is to determine what the state of law is with respect to a given set of facts at a certain time, typically now. Let’s return to the Dodd-Frank example above. Let’s say we’re in the compliance department at a financial institution and we’d like to know how the new proprietary trading rules affect us. To do this, we might perform the following tasks:
- Search for laws by concept, e.g., depository institution or derivative.
- Ensure that these laws are current and comprehensive.
- Build a set of rules or guidelines from these laws.
- Interpret these rules in the context of our facts.
However, the Statutes at Large is not well-suited to these tasks.
- It is sorted by date of enactment, not by concept.
- It contains laws that may affect multiple legal concepts.
- It contains laws that reference other laws for definitions or rules.
- It contains laws that amend or repeal other laws.
Based on our goal and these properties of the Statutes, we need to perform an exhaustive search every time we have a new question. This is pretty clearly bad if we want to get anything done (but hey, maybe you’re not in-house and you bill by the hour). So what might we do to re-organize the Statutes to make it easier for us to use the law?
- Organize the law by concept, possibly hierarchically.
- Combine laws that refer or amend one another.
- Remove laws that have expired or have been repealed.
- Provide convenient citations or identifiers for legal concepts.
A systematic organization of the Statutes at Large that followed these rules would make our lives significantly easier. We could search for concepts and use the hierarchical context of these results to navigate related ideas. We could rest assured that the material we read was near-comprehensive and current. Furthermore, we could communicate more succintly by referencing a small number of organized sections instead of hundreds of Public Laws.
As you might have guessed, this organizational scheme defines the United States Code as produced by the Office of the Law Revision Counsel. While the LRC traditionally distributes copies of the Code as ASCII files on CD-ROMs, they recently began distributing copies of the code in XHTML. We’ll be using these copies to build our index, so if you’d like to follow along, you should download them from here – http://uscode.house.gov/xhtml/.
If we’d like to build a legal search engine, the Code is arguably the best place to start. While there are other important statutory and judicial sources like the Code of Federal Regulations or the Federal Reporter, the Code is as close to capital-L Law as it gets.
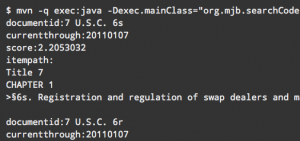 In this part of the post series, I’m going to build an index of the text of the Code from the 2009 and 2010 LRC snapshots. To do this, we’ll use the excellent Apache Lucene library for Java. Lucene is, in their own words, a “a high-performance, full-featured text search engine library written entirely in Java.” As we’ll see in later posts, Lucene (with its sister project, Solr) is a very easy and powerful tool to develop fast, web-based search interfaces. Before we dive into the code below the break, let’s take a look at what we’re working towards. Below is a search for the term “swap” across the entire Code. We’re displaying the top five results, and these were produced in a little over a second on my laptop. “
In this part of the post series, I’m going to build an index of the text of the Code from the 2009 and 2010 LRC snapshots. To do this, we’ll use the excellent Apache Lucene library for Java. Lucene is, in their own words, a “a high-performance, full-featured text search engine library written entirely in Java.” As we’ll see in later posts, Lucene (with its sister project, Solr) is a very easy and powerful tool to develop fast, web-based search interfaces. Before we dive into the code below the break, let’s take a look at what we’re working towards. Below is a search for the term “swap” across the entire Code. We’re displaying the top five results, and these were produced in a little over a second on my laptop. “
To view the images, click over to Michael Bommarito’s Blog (click here for direct access). Additional technical specifications and code are also available.
Ignite Law 2011 & The ABA Techshow
 On the eve the ABA Tech Show, I am looking forward to attending Ignite Law 2011 @ The Chicago Hilton. For those not familiar, Ignite offers a unique style of presentation (6 minutes total with automatically advancing slides). For a certain class of ideas, Ignite offers thefmaximal information compression approach to concept introduction. Anyway, the topics of the talks interesting.
On the eve the ABA Tech Show, I am looking forward to attending Ignite Law 2011 @ The Chicago Hilton. For those not familiar, Ignite offers a unique style of presentation (6 minutes total with automatically advancing slides). For a certain class of ideas, Ignite offers thefmaximal information compression approach to concept introduction. Anyway, the topics of the talks interesting.
Tomorrow, I will be attending some of the sessions at the Tech Show. If anyone is attending the conference and would like to touchbase, feel free to ping me.
The Patent Conference @ KU Law
Today, I am traveling to Kansas for The Patent Conference (aka Pat Con). Tomorrow, I will be presenting our methods paper Distance Measure for Dynamic Citation Networks (published in the Statistical Mechanics Journal – Physica A in October 2010). While the specific applied example in paper is focused on case-to-case legal citations, the formalization and method we present therein has general form applicability to all dynamic direct acyclic graphs (including the patent citation network). Thus, we are interested in discussing how to leverage our approach to better understand the path of innovation that is revealed in datasets such as the NBER patent dataset.